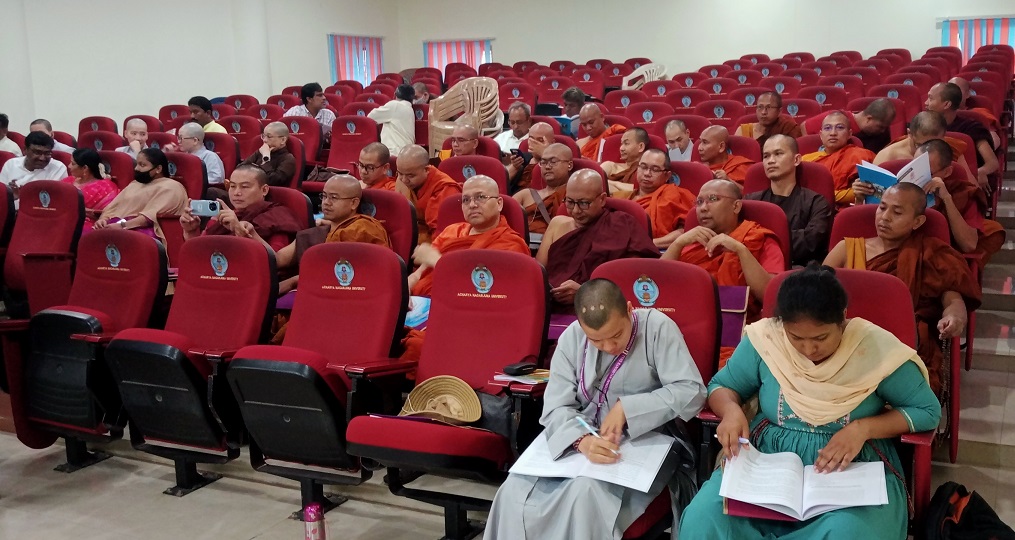
National seminar on “Minor Deities in Indian Art,” held at the C. P. Ramaswami Aiyar Institute of Indological Research, Chennai on March 28th and 29th 2024 (3).

28-03-2024 (Thursday): As I was expecting some photographs, I could not include them in the earlier postings and now included here. The paper, “The precept, concept and evolution of “minor deities” in India,” was presented first on the day with PPT. As only 15 minutes were given, it was wound up and completed. It covered the theme of the seminar, and it concluded with the following note:
Conclusion: In the Indian context, the question of “minor deities” covers thousands of years with many changes, modifications and incorporation. Thus, their representation in the art differs from time to time. Their position today as appearing in situ, at remote places, in the museums, temples functioning and deserted, inside and outside the temples and momentary worship for the occasion and all other exigencies also cannot decide the finality of the status of “minor deities”. In the modern context, to what extent, the syncretization, inculturation and inter-religious dialogue activities can be accepted has to be analyzed. They have to be two-sided and cannot be carried on in one way.

Only the believers of Gods and Goddesses have to be acceptable enough to accommodate all gods and goddesses, as they live in a secular state, if not a secular society. “If believers of Gods abuse Gods, seekers of Gods destroy Gods, faithful followers of one religion question the faith of others and, against all moral and ethical codes and universal principles, conduct pseudo-spiritual and psychological-religious warfare against another religion, then these activities are not “inculturation” but “outculturation”, as religion and culture are inseparable for Hindus[1].

“Theocentric and theocratic eclectics are as dangerous as nuclear, chemical and other warheads. The concept of “My God is your God, but your God is No God” does not foster understanding, co-operation and goodwill. The concept should be changed to “Your God is my God and my God is your God” and accepted by all religions…This is the only way for humanity today. Super God Rivalry, religious superiority, racial / arrogant theology, theocratic world domination and neo-spiritual globalism cannot make “believers” live in peaceful co-existence with others”[2].

In one way, the concept of “minor deities” creates an inferiority complex among the believers, as they have to accept the existence of “major deities.” However, when kuladevata worship comes, all have to go there to remote places without any discrimination. Thus, such deities continue forever, as long as the believers are there. Only the families should remember their kula-devatas.

29-03-2024 4 to 5 pm: Technical Session – VI was held at the Gallery, parallel and chaired by Dr. J. Soundararajan, Associate Professor & Head i/c Dept. of Ancient History and Archaeology, University of Madras and the following papers were presented:

Kandasami temple

The 27 sculptures there…

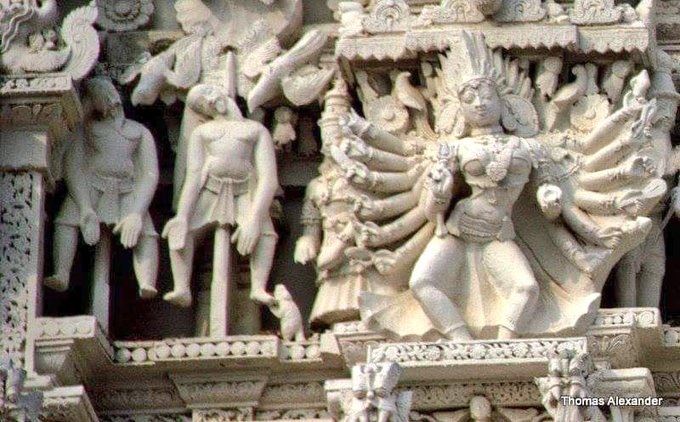
Sculptures of Vethalas

- Mrs. Geetha C[3] – “Vedhalas Worship in Cheyyur” – Cheyyur Kandaswamy temple is one of the Least Known temples of Tamilnadu. Cheyyur is a place that is located off the East Coast Road about 80 km from Chennai and the main deity of this temple is Lord Muruga who is worshipped as Kandaswamy. The Kandaswamy temple is an ancient temple that was built during the Chola period and it has no Gopuram at the entrance. The temple faces the South and the main deity faces the East. The main Lord of the temple is Sri Kandaswamy with his wives Valli and Devayanai.

There are 27 Vedalams (Bethals) on the inner side of the compound wall of the temple.[4]. These 27 Vedalams are found with their hands lifted up representing the 27 Birth Stars or Nakshatras worshipping Lord Muruga. These 27 Vedalams that are found here are believed to be the 27 Boodaganas who helped Lord Muruga in fighting the Demon Soorapadman. These 27 Vedalams obey the instructions of Lord Bhairava and so you can see the separate deity of Bhairava alongside the Vedalams. The day of Ashtami, that falls after the Full Moon is called ‘Theipirai Ashtami’. This day is considered to be more auspicious for Bhairava. On this day, the devotees worship the Vedalam that represents their Birth star. On the day of Theipirai Ashtami, the Vedala pooja usually starts with Vinayaka Sankalpa, followed by special Archanai for the Vedalams with Red Arali (Nerium) flower. Then it will be followed by Abishekam and Special Archanai for Bhairava with 8 different types of flowers.



- Mrs. C. Uma[5] – “Kubera – The Lord of Wealth and his influences in Indian Society” – Kubera – कुबेर, also known as Kuvera, Kuber and Kuberan, is the god of wealth, and the god-king of the semi-divine yakshas in Hinduism. He is regarded as the regent of the north (Dikpala), and a protector of the world (Lokapala). His many epithets extol him as the overlord of numerous semi-divine species, and the owner of the treasures of the world. Kubera is often depicted with a plump body, adorned with jewels, and carrying a money-pot and a club. Originally described as the chief of evil spirits in Vedic-era texts, Kubera acquired the status of a deva (god) only in the Puranas and the Hindu epics. The scriptures describe that Kubera once ruled Lanka, but was overthrown by his half-brother Ravana, later settling in the city of Alaka in the Himalayas. Descriptions of the “glory” and “splendour” of Kubera’s city are found in many scriptures. Kubera has also been assimilated into the Buddhist and Jain pantheons. In Buddhism, he is known as Vaisravana, the patronymic used of the Hindu Kubera and is also equated with Pañcika, while in Jainism, he is known as Sarvanubhuti.

- K. Bakialakshmi[6] – Jyestha (Thavvai) – Jyestha or Jyeshtha = ज्येष्ठा, Jyeṣṭhā, “the eldest” or “the elder”) is the Hindu goddess of adversity and misfortune. She is regarded as the elder sister and antithesis of Lakshmi, the goddess of prosperity and auspiciousness. She is commonly referred to as Moodevi in South India. Jyestha is associated with inauspicious places and sinners. She is also associated with sloth, poverty, sorrow, ugliness, and often depicted with the crow. She is sometimes identified with Alakshmi, another goddess of misfortune. Her worship was prescribed for women, who invoked her to keep her away from their homes. Jyestha appears in the Hindu tradition as early as 300 BCE. Her veneration was at its peak in South India in the 7th-8th century CE. By the 10th century, her popularity had waned, pushing her into oblivion. Today, numerous ancient images of Jyestha still exist, though she is seldom worshipped. She tried to equate Jyesta with Thavvai (Muthevi, Muthadevi etc) with sculptures of Tamilnadu. Nowadays, learned bloggers have been blogging on different subjects in detail and they can be converted into a book. For example, about this subject, a seven-part blog is available with all information, photos and other details in Tamil[7].
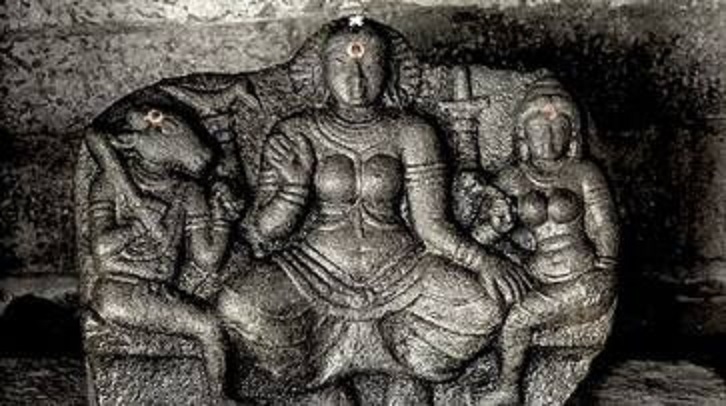

Tavvai sculpture found in Tamilnadu abandoned at several places……

- Ms. S. Nithya[8] – “Iconography of Vārāhi” – Varahi = वाराही, is one of the Matrikas, a group of seven mother goddesses in the Hindu religion. Bearing the head of a sow, Varahi is the shakti (feminine energy) of Varaha, the boar avatar of the god Vishnu. In Nepal, she is called Barahi. In Rajasthan and Gujarat, she is venerated as Dandini. Varahi is more commonly venerated in the sect of the Goddess-oriented Shaktism, but also in Shaivism (devotees of Shiva) and Vaishnavism (devotees of Vishnu). She is usually worshipped at night, using secretive Vamamarga Tantric practices. The Buddhist goddesses Vajravārāhī and Marichi have their origins in the Hindu goddess Varahi. She tried compare the sculptures, but could not differentiate among the Jain, Buddhist, Hindu and other splinter tantric groups.

Varahi sculpture……..

When many research materials are available in the public domain research has to be new, different and appropriate: If any person, serious researcher, professor or an expert of the discipline attending conferences, seminars, congress or workshop continuously, he / she could find out that how papers are repeated with the material that is already available. The paper presenters, papers who prepares or researcher doing studies on any subject could also find such materials are available already in the public domain. After the advent of internet and the digitization of papers and books, anyone can easily access them. So also others, thus, the source, authenticity and veracity can be verified very easily. Nowadays, the plagiarism software points out, and it has become a tedious process of revising the PhD thesis again and again. The flow, way of expression and writing language also play important role, where the researcher has to maintain his / her individuality. Therefore, the paper presenters should be judicious enough to take sources, use them properly and come out with new findings or at least new interpretation.
Research should be judicious and independent without bias: Research cannot be putting the “result” first and then finding the source or the supporting materials. Such researcher always tempts to take the material that is favourable and reject or ignore that is not required or against his “result.” The researcher has to follow the rule of “audi alterum partem” (to hear / listen the other side). Thus, a well-seasoned, unbiased and balanced researcher would go into all sources and learn from them. Suppose, if his hypothesis is wrong, then, definitely, he has to change the topic. How Newton discovered the Law of Gravitation, just by looking at the falling apples? Were apples flying in the sky instead of falling on the ground before? No, not at all. Therefore, thinking new is very much essential for a researcher, that too, different from others.
Academically conducted seminar: CPRIIR has self-contained expertise for conducting seminars, conferences and congresses also for many years. I have been attending for the last 30 years. The Director and the staff have been well-trained and they conducted the seminar academically giving an opportunity to the paper presenters. They have been meticulous in carrying out the programme very systematically. I had a feeling, as if I was there on Saturday also!
© K. V. Ramakrishna Rao
30-03-2024.

[1] K. V. Ramakrishna Rao, Pollution of Hinduism, a letter appeared in Indian Express, March 28, 1989.
Collins, Paul. “The Praxis of Inculturation for Mission: Roberto de Nobili’s Example and Legacy.” Ecclesiology 3.3 (2007): 323-342.
[2]Sita Ram Goel, Catholic Ashrams, (Letter published in Indian Express March 28, 1989), Voice of India, New Delhi, 1994, p.161. Also, see here: http://voiceofdharma.com/books/ca/ch14.htm
[3] Abstracts, sl.no. 15; p.36.
[4] Cheyyur Kandaswamy Temple – An Unique Temple With 27 Birth Star Vedalams – https://gosthala.com/cheyyur-kandaswamy-temple-a-temple-with-27-birth-star-vedalams/
[5] Abstracts, sl.no. 33; p.53.
[6] Abstracts, sl.no. 13; p.27.
[7] Vedaprakash, Muthevi, Muthadevi, Tavvai, Mundadevi etc., September 2018;
- https://indianhistoriography.wordpress.com/2018/09/11/mudhevi-claiming-as-tamil-goddess-with-race-racial-and-racist-theories/
- https://indianhistoriography.wordpress.com/2018/09/11/lakshmi-alakshmi-interpreted-by-dravidian-writers-without-any-basis-mudevi/
- https://indianhistoriography.wordpress.com/2018/09/12/mudevi-tamil-experts-write-without-caring-for-historical-evidences-and-chronology/
- https://indianhistoriography.wordpress.com/2018/09/12/mudevi-caught-in-aryan-dravidian-race-interpretation-without-historical-evidence/
- https://indianhistoriography.wordpress.com/2018/09/12/tamil-writers-do-propaganda-without-any-historical-evidences-delving-upon-aryan-dravidian-myths/
- https://indianhistoriography.wordpress.com/2018/09/12/vamacharya-amorous-sculpture-and-biased-research-mislead/
- https://indianhistoriography.wordpress.com/2018/09/12/mudevi-muttadevi-thavvai-jyestha-devi-dravidian-witers-confusing-and-misleading-without-historical-evidences/
[8] Abstracts, sl.no. 19; p.35.
Filed under: middle deity, minor deities, minor deities in indian art, minor deity, minor god, minor goddess, minority deity, monument, morality, mother goddess, orientation, orissa, sangam, sangam literature, sangam period, sectarian, sectarian faith, sectarianism, soul, stigma, story, system, tamil, tamili, Tantra, temple, terracotta, terracotta figurine, Tianzhu, trade, uncivilized, University of Madras, updating, Vayu, Veda, Vedas, Vedic, vedic astronomy, vedic chronology, vegetarian, vijayanagar, Vijayanagara, Vishnu, votive, vyasa, Vyasaraja, wheel, woman, yagna, Yantra, Yogic, Yogini, youth | Tagged: deity, God, goddess, Hinduism, history, India, major deity, majority deity, middle deity, minor deity, minority deity, religion, travel | Leave a comment »