The proceedings of the National seminar Buddhism and Sectarian Religious faith in India or Buddha and Anti-caste Bhakti Saints held at Acharya Nagarjuna University on March 1st and 2nd 2023 (4)
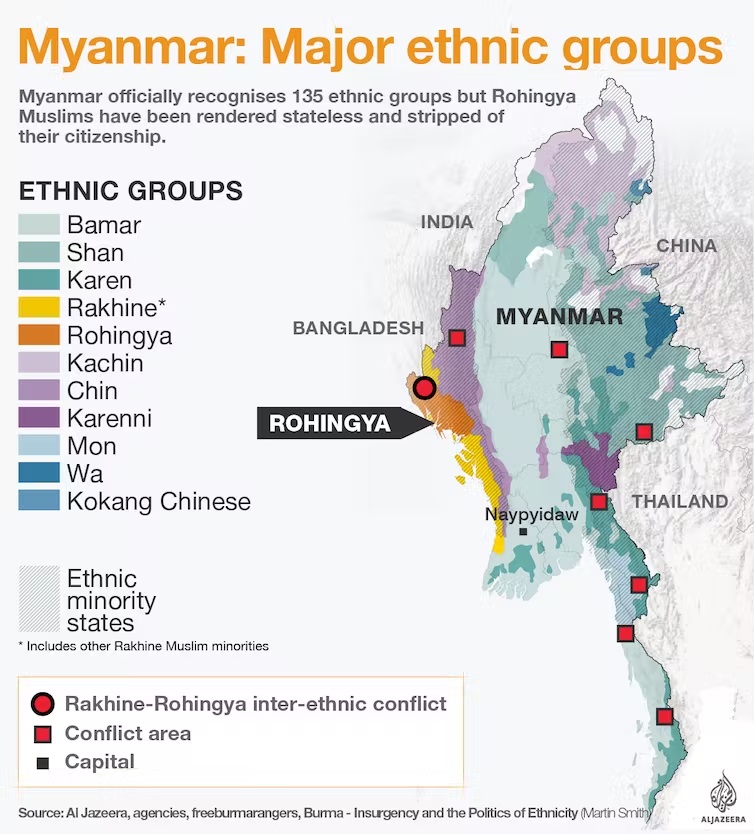
Caste system in Burma / Myanmar: The Burmese authorities presently recognise no fewer than 135 separate ethnic groups out of 55 million population, living within the union. Of these, the Bamar are easily the largest. Myanmar’s first national census in over 30 years. The other six main ethnic groups are –
| 1. the Shan, 2. Kachin, 3. Kayin, | 4. Rakhine, 5. Chin and 6. Mon, |
each of which has its own state. These seven main ethnic groups together constitute about 92 per cent, with the remaining 8 per cent divided between a fascinating patchwork of minority tribes. Jane Fergusson discussed the issue as follows[1]: The system of caste, or a hierarchical social system based on occupation, prestige, and ideas about pollution, had been considered a master trope in the framing of the imperial census[2] (Kumar 2006:387), and one which colonial officers had grown accustomed to in British India. Census officials even noted that caste could be tested by ‘actual existing facts and beliefs to a far greater extent than is possible with respect to race’ (Webb[3] 1912:250). However, the categories of caste simply did not gain traction for census officials working in Burma; thus they struggled to find another way to approach human differences and quantify race in Burma. The nine ‘race’ categories used by the British census-takers were:
| 1. Burmese; 2. Other indigenous race; 3. Chinese; | 4. Indians born in Burma; 5. Indians born outside Burma; 6. Indo-Burman race; | 7. Europeans and allied races; 8. Anglo-Indians; 9. Other race. |
According to C.C. Lowis[4] (1902), the Burman is ‘so absolutely enamoured of freedom that he cannot abide the bonds that caste demands’ (Lowis 1902:107). Without the category of caste, and where religion ‘indicates but little’, colonial surveyors concluded that language would therefore be the most ‘obvious and surest criterion of difference’ (Lowis 1902:112): If the speech of a particular community cannot be assigned to a particular group, that community is, ipso facto, isolated, whatever similarity its customs, dress and physical traits may have with the customs, dress and physical traits of any other community, neighbouring or otherwise.

Caste thennic groups, ethnicity, denomination, sect and such other classification based on race, racism and racialism, religion, theology, philosophy etc., exist in Thailand……..

Sectarian, sectarianism, sectarian faith etc: The words and sect, expressions sectarian, sectarianism, sectarian faith etc., have not been positive, but negative and bad in connotation in the western or western religious context. Throughout American history, “sectarian” has been used to exclude and to ostracize. It is a term that is used to disparage and marginalize particular groups of Americans and particular kinds of thinking. That “sectarian” is hardly a flattering term is evident from even a cursory look at any standard dictionary. Among its more common synonyms are “bigoted,” “narrow-minded,” “heretical,” “parochial,” and “dogmatic.” Christians have used the word to describe Pharisees, atheists, and other Christians; Unitarians to put down Presbyterians and Roman Catholics; political liberals and conservatives to insult each other[5]. Richard A. Baer, Jr explains that[6], “The reason is really quite simple. Even though the term “sect” can have the relatively neutral meaning of “a group of persons having the same principles, beliefs, or opinions or can be employed technically in a non-pejorative sense by sociologists of religion, the ordinary usage of “sectarian” is derogatory. Indeed, “sectarian” more often than not is what we might call “caste language.” It is a term that has been used throughout much of American history to keep religious and social “untouchables” in their proper place. Just as ruling elites have used racial and sexual epithets to put down blacks and women, so they have used “sectarian” to exclude and marginalize those individuals and groups whose religious or philosophical beliefs or social practices did not correspond to their own vision of what was appropriate in the cultural marketplace”.

The theme of the seminar changed from “Buddhism and Sectarian Religious faith in India,” to “Buddha and Anti-caste Bhakti Saints”: Though, the topic was “Buddhism and Sectarian Religious faith in India,” (as appeared in the brochure first) most of the paper presenters were trying to interpret the present ideology on the medieval period and even the prehistoric and protohistoric past. It also appears that the theme was changed to “Buddha and Anti-caste Bhakti Saints” suddenly, as noted later on the banner, “Abstract,” scribbling pad etc. Actually, I prepared my paper only based on the such theme and sent my full paper on 31-01-2023 itself. The theme, “Buddhism and Sectarian Religious faith in India,” has been entirely different from that of, “Buddha and Anti-caste Bhakti Saints.” It is a fact that during the transitional period 7th century to the medieval period till the advent of the Mohammedans and the European colonial forces, all the sectarian faiths had to suffer by them. The ruling and dominant faiths Janism and Buddhism had to suffer from their attacks, in spite of their oversea and inland business and commercial authority. When religious dominance and excesses started, these two could not match up with them (Islam and Christianity). Moreover, the interaction among the believers of Andhra, Karnataka and Tamilagam showed the intra and inter-faith and religious debates, polemics and wrangles, leading to physical sometimes. Obviously, the organizers must have realized from my paper and changed the theme. Therefore, it is evident that they changed the theme itself, perhaps, without informing.

Under the Ambedkarite Constitution, Caste should continue or not: Eleanor Zelliot (1992), Uma Chakravarthi (1996), Gail Omvedt (2003) and others cleverly avoided the continuance of caste in spite of opposing caste, supporting reservation, though opposing positive discrimination, exclusion etc., Thus, the ideological egalitarianism, theoretical Utopianism and sermonized equality always try to and evade the legal, constitutional and judicial position and condition of the prevalent issues. The restricted reservation for SCs has been continuing. The reservation after conversion for the neo-Buddhists, and Sikhs continues, as they are “Hindus” only as per Article 25 of the Constitution. Thus, the Christians and much later the Muslims too started demanding the amendment of the Constitution Order, 1950 to accommodate the converted Christians and Muslims also. Though, these ideologists claim that “The Ambedkar Constitution,” they want to amend it, without realizing the judicial implications.

What is required by the believers in a “Secular state or country”?: Dialogue is required for understanding other and the point of view of others, whether, in a family, society or anywhere, where human interaction takes place. Thus, it is imperative and implied that such a process is possible with all family and societal members. Discussion, debate and deliberation always involve mutual, reciprocated and two-way flow of thought, thought processes and conclusion. Monologue is considered as a speech presented by a single dramatist character, theoretical expert or ideologized professional most often to express their thoughts aloud, though sometimes also to directly address another character or the audience. In theatre, a monologue may be enjoyed when delivered by favourite character or person, as none is going to ask him. Monologues are common across the range of dramatic media (plays, films, etc.), as well as in non-dramatic media such as poetry, literary narratives, political discourses and other verbose. Monologues share much in common with several other literary devices including soliloquies, apostrophes, and asides. There are, however, distinctions between each of these devices, audience and ideologists. Many times such monologues, particularly thrusted, imposed and forced to listen lead to autocratic, dominating and dictatorial. Free speech is talked about and sermonized blaming others as despotic, tyrannical, repressive, oppressive and so on, but, how such whistle-blowers indulge.

In dialogue, the engaged parties should listen to and understand the other party / parties also: There is a maxim Audi Alteram Partem and it is not known whether monologuers could understand and realize it. It means hear the other side; hear both sides, in other words the authority hearing the matter must be afforded hearing to the party who is likely to be affected by its decision. In judicial, quasi-judicial or any sensible legal process, it is expected. Therefore, those who talk about thesis, anti-thesis and synthesis should not avoid or be afraid of Audi Alteram Partem. Here, most of the speakers have predetermined mind-set and they spoke even any prepared paper about certain premises and conditions only in their perspective, that too blaming Brahmin, Brahman, Brahminism, Brahminical system, and even Brahminical virus and so on. Inside, “Acharya Nagarjuna University,” though such seminar was taking place under the auspices of “The Mahayana Buddhist Study Centre,” the sectarian bias had been explicit and aggressive and combating.

Justice, natural justice, social justice, equity, equality etc: Though, often Justice, natural justice, social justice, equity, equality etc, are talked about, they are not obviously discussed judicially. There are mainly two Principles of Natural Justice. These two Principles are:
- ‘Nemo judex in causa sua’. No one should be made a judge in his own cause, and the rule against bias.
- ‘Audi alteram partem’ means to hear the other party, or no one should be condemned unheard.
The historians, archaeologists, anthropologists, archaeo-anthropologists, Anthropo-archaeologists, sociologists, psychologists and related experts do not deal with these important conditions to pass any remarks or come to conclusions. Going to extremes, violating the norms that are framed the ideologists by themselves, and jumping to conclusions with biased views have been the hall-mark of many such studies.

How the audience was responding to the Buddhist prayer……..

How the audience was responding to the Buddhist prayer…………………..

How I struggled to reach and left Vijayawada Railway Station: How I reached Vijayawada Railway station was explained above on Fenbruary 28th midnight and March 1st early morning. On 2nd March also, I had a different experience to reach the Vijayawada station. The seminar paper presentation was going on, as I had to catch the train, I came out of the hall searching for the driver. He was there, and we had lunch quickly and about to leave, but, I was informed that some other driver and vehicle would come. So I was waiting…….and the time was 2.00 pm. I asked the convener many times and I was informed “the vehicle would come.” It was 2.30 PM and then, realizing the situation, I was taken by a car. Of course, the driver and car were there only[7]. Anyway, the driver could drop me at the end of the platform, so that I could walk to the platform[8]. Slowly, I started walking with the bag to the Platform No.10 where, the JanSatabdi was to come. When I reached PF.No.10, the passenger started running back, shouting at me, that it was here at PF.No.8. Some stranger helped me taking my bag and I started walking slowly. It took me perhaps 10 to 15 minutes and the train was about to start. I was waving my hand towards the train, as if I was doing it for a bus to stop. But, the driver was looking at me and showed his finger “1,” obviously, he might wait for one minute. Meanwhile that stranger handed over my bag to another stranger and went away. When I came near to the train, he (the second stranger) suggested me to gt into the first carriage and pushed my luggage inside. The moment I entered the train and started requesting to the TTR, one youth asked me to sit in one seat, as he was not travelling and got down……….The train started…..So finally, I settled down there in the same compartment, instead of my regular / confirmed seat away from the first compartment[9]. At last I could reach Chennai with 20 minutes delay. My regular Auto driver came and I could reach home by 11.40 PM.
© K. V. Ramakrishna Rao
05-03-2023

[1] Ferguson, Jane M. “Who’s Counting?: Ethnicity, Belonging, and the National Census in Burma/Myanmar.” Bijdragen tot de taal-, land-en volkenkunde/Journal of the Humanities and Social Sciences of Southeast Asia 171.1 (2015): 1-28.
[2] Kumar, M. Satish (2006). ‘The census and women’s work in Rangoon, 1872–1931’, Journal of Historical Geography 32:377–97.
[3] Webb, C. Morgan (1912). Census of India, 1911. Vol. ix, Burma Part i. Report. Rangoon: Office of Superintendent, Government Printing and Stationery.
[4] Lowis, C.C. (1902). Census of India, 1901. Volume xii, Burma. Part i. Report. Rangoon: Office of Superintendent, Government Printing and Stationery
[5] Richard A. Baer, Jr. The Supreme Court’s Discriminatory Use of the Term “Sectarian”, Originally published in The Journal of Law & Politics, Vol. VI, No. 3, Spring 1990.
[6] https://blogs.cornell.edu/envirobaer/publications/the-supreme-courts-discriminatory-use-of-the-term-sectarian/
[7] In other words, instead of keeping me waiting there for nearly one-and-half hours, I could have been sent earlier with the same driver and car. Why I was kept delayed was known to God only.
[8] Actually, the driver helped me in reaching the station in time and also dropping at the right place. Of course, when we reached the Guest House to take the luggage, the other person / Assistant Professor was making unwanted comments that I would miss the train and so on. Though, he had also to come with me, he was delaying, so the driver took the decision to proceed, as the time was already 2.30 PM. Why the learned Asst.Prof was delaying was also known only to God.
[9] I can write a story about this, as how many strangers helped me to get into a train, sit comfortably in a seat and reach my home at one side, whereas, at the other side – all learned professors etc., but made me tensed fully knowing my health problems. Of course, I informed my travel plan, my health problem etc through e-mails and letter also (with many phone calls in between).

Filed under: A case for India, A.A. Fuhrer, academic, academicia, Acharya, Acharya Nagarjuna University, adi sankara, agnostic, agony, agrarian, agriculture, ahimsa, ambedkar, ambedkar idea, ambedkar ideology, ambedkar philosophy, ambedkar thought, anthropology, anti-brahman, anti-brahmin, anti-caste, anti-hindu, anti-india, anti-indian, anti-vedic, archaeological remains, archaeological sites, archaeology, Ariyar, Art and Culture of Tamil Nadu, arya, Aryan, ascetic, astronomy, atheistic, atma, ayodhya, Ayodhya issue, Babari Masjid, beef, begging, bharat, Bharat-centric, bias, Brahma, brahman, Brahmi, brahmin, Buddhist, buddhist claim, Buddhist relic, buddhist site, caste, chaitya, child marriage, chronology, civilization, colony, colour, Communist Historian, compassion, conduct, constitution, controversy, daispora, dalit, dalit buddhhist, dalit Buddhist, dalit christian, dalit hindu, dalit Jain, dalit literature, dalit muslim, Damila, date of Asoka, date of Buddha, date of Sankara, demolition, demonstration, demythologization, depressed class, desecration, discrimination, Dramila, Dravida, Dravidam, dravidar, Dravidi, Dravidian, emotion, ethnicity, ethnology, ethnos, female, female infanticide, female-worker, feminist, freedom of expression, freedom of thought, gnostic, hindu ritual, Hinduism, historian politician, historical politician, historicity, historiography, historiosophy, history, history usage, history useful, iconoclasm, iconogenesis, ideological, ideology, idol, inculturation, jain, jain persecution, jainism, jains persecuted, K. V. Ramakrishna Rao, karma, language, last rites, linguistics, mandal, marxism, Marxist historian, Marxist-Leninist, myth promoted, mythologization, mythology, nation, nation building, nation-building, nation-state, non-brahmin, non-Veddc, non-Vedic, non-vegetarian, non-violence, not Hindu, race, racialism, racism, reform, reformation, refutation, regionalism, Saivam, Saivism, Sangam, sangam, Sangam literature, sangam literature, sangam period, sati, SC, scheduled tribe, social justice, social reform, Social Reform Movement, Social Reform Movement In India, social reformation, Social science, tamil separatism, tamil siddha, Tamil siddha manuscript, Uplift of women, Upliftment of Dalits, Vedas, Vedic, vedic astronomy, vedic chronology, veera savism, vegetarian | Tagged: acharya nagarjuna, Acharya Nagarjuna University, ambedkar, ambedkar chair, ambedkar philosophy, ambedkarism, ambedkarite, anti-caste, ariyan, Ariyar, arya, aryan, aryan invasion, aryan race, B.R.Ambedkar, bakti, bhagawat gita, bhakti, bhakti movement, brahmin virus, brahminical diaspora virus, buddha, buddhism, Buddhist, buddhist claim, buddhist site, carona virus, caste, caste conflict, caste politics, caste virus, casteism, dalit, dalit Buddhist, dalit christian, dalit hindu, dalit Jain, dalit liberation, dalit literature, dalit muslim, dalit politics, gail omvedt, scheduled caste, uma chakravarti, Upliftment of Dalits, virus | Leave a comment »












































